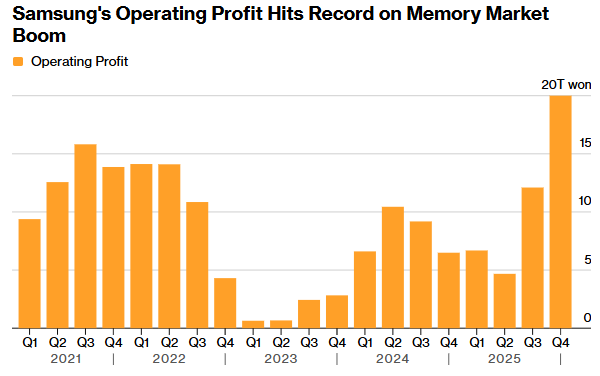
AI spawned a “memory shortage” and a “wave of storage price increases” detonated Samsung's Q4 performance: operating profit increased 208% year-on-year, and revenue reached a new high
The Zhitong Finance App learned that Samsung Electronics' quarterly profit has more than tripled, reaching a record high, as global demand for artificial intelligence servers has greatly boosted the price of memory chips. In the three months ending December, Samsung Electronics' initial operating profit was 20 trillion won (US$13.8 billion), up 208% year over year, exceeding analysts' average expectations. Revenue increased 23% to 93 trillion won, which also reached a record high. The company's stock price rose 2.5% in early Thursday trading in Seoul, continuing the 20% increase since the beginning of the year. Rival SK Hynix's shares rose 6.2%.
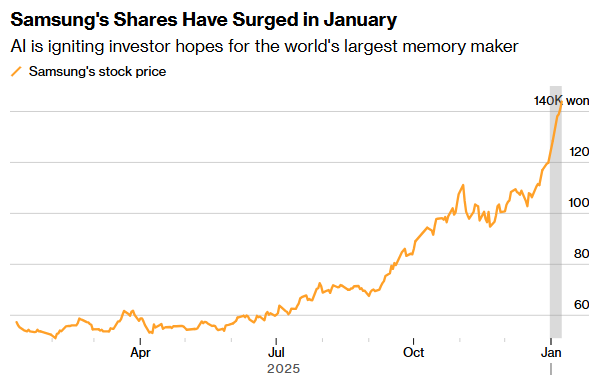
Samsung's stock price has more than doubled in value in 2025 and soared again this month, reflecting the market's expectations that Samsung's performance will be very successful this year after competitor Micron Technology (MU.US) issued an optimistic forecast. Last week alone, more than 10 analysts raised Samsung's target price. The company will provide a complete financial statement with net profit and division details on January 29.
Jeff Kim, head of research at KB Securities, said that emerging fields, including humanoid robots and driverless cars, require memory, and devices that flaunt artificial intelligence capabilities are also driving a sharp rise in demand for DRAM and NAND. He said, “It's still too early to talk about spikes in demand; investors should buy and hold memory stocks. If the stock price falls after the profit reaches 20 trillion won, it is a good time to buy.”
This week, Samsung executives emphasized the seriousness of the shortage of memory chips at the CES Consumer Electronics Show. President Lee Jae-rong said that the prices of consumer electronics products have already begun to rise, and “there will be problems with semiconductor supply.”
Counterpoint Research predicts that the price of DDR5, the latest generation of traditional DRAM used in computers and servers, will rise 40% this quarter compared to the previous three months, and another 20% increase in the second quarter.
According to the analysis, Samsung's initial operating margin reached 21.5% in the fourth quarter of 2025, indicating that it will benefit from strong market demand for traditional DRAM, high-bandwidth memory (HBM), and NAND flash memory chips. DRAM's operating margin may exceed 50% in the fourth quarter and is expected to increase further in the first quarter of 2026; traditional DRAM contributed high revenue to Samsung. Its leading position in the global NAND flash memory chip market will also help it achieve profit growth in 2026.
Samsung, which has always lagged behind SK Hynix and Micron in the field of high-bandwidth memory, delivered its advanced HBM4 samples to Nvidia for certification testing last year. This has fueled hope that Samsung may be able to close the gap with competitors and begin mass production of the HBM4 in the first half of this year to support Nvidia's upcoming Rubin processor. Analysts expect Samsung's total HBM shipments to triple in 2026 as HBM4 enters the commercial supply phase.
 Index Options
Index Options State Street
State Street CME Group
CME Group Nasdaq
Nasdaq Cboe
Cboe TradingView
TradingView Wall Street Journal
Wall Street Journal