Is East Japan Railway Company's (TSE:9020) 7.8% ROE Better Than Average?
Many investors are still learning about the various metrics that can be useful when analysing a stock. This article is for those who would like to learn about Return On Equity (ROE). We'll use ROE to examine East Japan Railway Company (TSE:9020), by way of a worked example.
ROE or return on equity is a useful tool to assess how effectively a company can generate returns on the investment it received from its shareholders. In other words, it is a profitability ratio which measures the rate of return on the capital provided by the company's shareholders.
How Is ROE Calculated?
The formula for ROE is:
Return on Equity = Net Profit (from continuing operations) ÷ Shareholders' Equity
So, based on the above formula, the ROE for East Japan Railway is:
7.8% = JP¥233b ÷ JP¥3.0t (Based on the trailing twelve months to September 2025).
The 'return' is the profit over the last twelve months. So, this means that for every ¥1 of its shareholder's investments, the company generates a profit of ¥0.08.
See our latest analysis for East Japan Railway
Does East Japan Railway Have A Good ROE?
Arguably the easiest way to assess company's ROE is to compare it with the average in its industry. The limitation of this approach is that some companies are quite different from others, even within the same industry classification. You can see in the graphic below that East Japan Railway has an ROE that is fairly close to the average for the Transportation industry (7.2%).
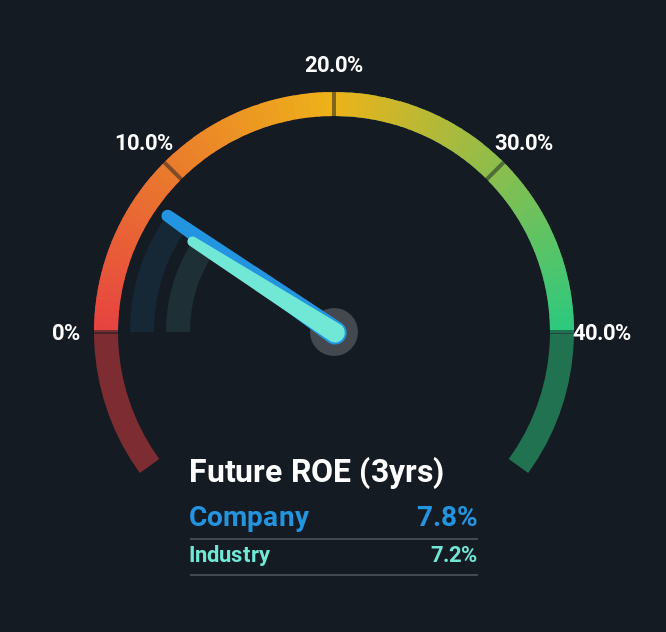
That isn't amazing, but it is respectable. While at least the ROE is not lower than the industry, its still worth checking what role the company's debt plays as high debt levels relative to equity may also make the ROE appear high. If so, this increases its exposure to financial risk.
Why You Should Consider Debt When Looking At ROE
Most companies need money -- from somewhere -- to grow their profits. That cash can come from retained earnings, issuing new shares (equity), or debt. In the case of the first and second options, the ROE will reflect this use of cash, for growth. In the latter case, the use of debt will improve the returns, but will not change the equity. In this manner the use of debt will boost ROE, even though the core economics of the business stay the same.
Combining East Japan Railway's Debt And Its 7.8% Return On Equity
East Japan Railway clearly uses a high amount of debt to boost returns, as it has a debt to equity ratio of 1.60. The combination of a rather low ROE and significant use of debt is not particularly appealing. Debt increases risk and reduces options for the company in the future, so you generally want to see some good returns from using it.
Conclusion
Return on equity is a useful indicator of the ability of a business to generate profits and return them to shareholders. Companies that can achieve high returns on equity without too much debt are generally of good quality. If two companies have the same ROE, then I would generally prefer the one with less debt.
But when a business is high quality, the market often bids it up to a price that reflects this. It is important to consider other factors, such as future profit growth -- and how much investment is required going forward. So you might want to take a peek at this data-rich interactive graph of forecasts for the company.
Of course, you might find a fantastic investment by looking elsewhere. So take a peek at this free list of interesting companies.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
 Index Options
Index Options State Street
State Street CME Group
CME Group Nasdaq
Nasdaq Cboe
Cboe TradingView
TradingView Wall Street Journal
Wall Street Journal