Bank of America: The global smart glasses competition has accelerated China's firm occupation of the manufacturing center
The Zhitong Finance App learned that with the intensive launch of new smart glasses by tech giants such as Meta, the industry is reaching a “tipping point”. On September 22, Bank of America released a research report stating that artificial intelligence glasses (AI glasses) will lead growth in 2025-2027, and augmented reality glasses (AR glasses) are expected to take over as the core driving force from 2028; while China will occupy a key role in the global smart glasses supply chain with over 80% of suppliers and a manufacturing center position. In the report, Bank of America listed companies such as Goertek (002241.SZ), Crystal Optoelectronics (002273.SZ), and Shunyu Optics (02382) as core beneficiaries.
Industry trends: From “AI first” to “AR led”, shipment growth can be expected
Bank of America analysts judged in the research report that the smart glasses industry has entered the phase of accelerated demand release, and the core growth logic shows the characteristics of “two-stage differentiation”:
Phase 1 (2025-2027): AI glasses lead growth
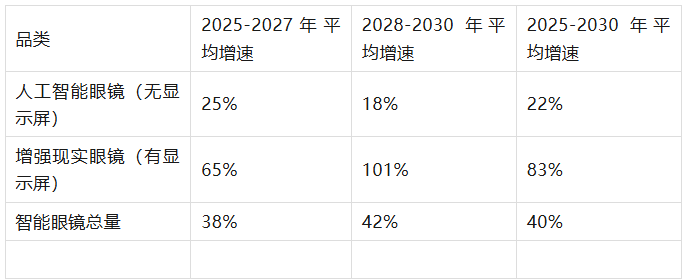
AI glasses without displays will be the first to become mainstream in the consumer market due to their high technical maturity and controllable cost. They are mainly used in lightweight scenarios such as voice interaction, environmental perception, and health monitoring. At this stage, AI glasses shipments are expected to grow at an average annual rate of 25%.
Phase II (from 2028): AR glasses take the lead
As the cost of display technology (such as Micro OLED) and optical solutions (such as optical waveguides) decreases and computing power increases, AR glasses with displays will gradually replace AI glasses and enter complex scenarios such as navigation, industrial assistance, and immersive interaction. The average annual growth rate of AR glasses shipments is expected to reach 101%.
Looking at the overall market, the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of global smart glasses shipments from 2025 to 2030 will reach 40%. Among them, around 2027 is expected to usher in a “doubling inflection point” in shipments, mainly driven by the consumer electronics switching cycle, the implementation of enterprise-level applications, and ecological investment by technology giants.
Supply chain pattern: China is the core manufacturing base, EMS extends to Southeast Asia
The global smart glasses supply chain is characterized by “China dominance and regional division of labor”. The specific layout is as follows:
Supply side: Chinese companies control over 80% of core links
From components to complete machine assembly, Chinese suppliers cover key fields such as cameras, optical waveguides, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), and batteries. Among them, camera modules (Shunyu Optics), optical coatings (crystal optoelectronics), and complete machine assembly (Goertek) all account for more than 50% of the global market share.
Manufacturing side: China is the core, EMS expands to Southeast Asia
Currently, the main manufacturing bases of global smart glasses are concentrated in China (such as Weifang, Shandong, and Shenzhen, Guangdong), but in order to avoid supply chain risks, electronic manufacturing service (EMS) companies are gradually shifting some non-core assembly links to Southeast Asian regions such as Vietnam and Malaysia, and production of core components remains in China.
Technical barriers: focus on “efficient delivery + adaptability”
The industry's core competitive focus is on two major technical directions: one is drug delivery efficiency (such as optical transmittance of AR glasses, voice recognition accuracy of AI glasses), and the other is user adaptability (such as lightweight design, battery life, and matching usage scenarios for different groups of people). Companies with core technology patents will establish differentiation barriers.
Key Company Analysis: Ratings and Valuation Logic
Bank of America gave clear ratings and target prices for the three core targets based on “supply chain position+technical barriers + growth certainty”. The details are as follows:
1. Goertek shares - global assembly leader, upgraded to “buy”
Core advantage: The world's largest smart glasses assembler, accounting for more than 70% of assembly orders from leading customers such as Meta and Sony; it also has the ability to self-develop core components (such as acoustic modules), and the degree of vertical integration is higher than that of peers.
Price target basis: Based on the 2026 expected price-earnings ratio (PE) of 34 times (consistent with historical XR industry upward cycle valuations), the target price is set at RMB 42. The valuation takes into account the expected average annual growth of 30% in the smart glasses assembly business from 2025 to 2027, as well as the increase in profit margins brought about by the parts business.
Risk warning:
Downside risks: AirPods market share is being eroded by competitors (affecting short-term cash flow), AR/VR business growth falls short of expectations, and macroeconomic deterioration leading to weak consumer electronics demand;
Upside risks: Profit margins are improving faster than expected, smart glasses shipment growth breakthroughs are predicted, and orders from new customers (such as Apple and Google) have been placed.
2. Crystal Optoelectronics — AR optical core, maintaining “buying”
Core advantage: The core supplier of optical waveguide sheets for AR glasses uses the “nano imprinting + coating” process, and the product transmission rate reaches 92% (industry average 85%); at the same time, it also lays out 3D sensing lenses and periscope lenses, which can collaborate with the smart glasses business.
Price target basis: Based on the expected price-earnings ratio of 27 times in 2026 (historical trading average), the target price is set at RMB 30. The core logic supporting the valuation is that the company's profit compound annual growth rate stabilized at 22% from 2024-2027, and the increase in orders due to the increase in the penetration rate of AR glasses.
Risk warning:
Downside risks: the penetration rate of 3D sensing lenses and periscope lenses falls short of expectations, weak consumer electronics demand, and slow automotive head-up display (HUD) /LiDAR (LiDAR) business development;
Upside risk: Increased profit margins due to orders for AR eyewear waveguide exceeding expectations, recovery in consumer electronics demand, and easing of industry competition.
3. Shunyu Optics — camera/optical waveguide dual-wheel drive, maintaining “buying”
Core advantages: Smart glasses core camera module supplier (global market share exceeds 60%), and also enters the field of optical waveguides to form “optical device+module” integration capabilities; the automotive ADAS camera business can provide technical collaboration for smart glasses (such as low power imaging algorithms).
Price target basis: Based on the projected price-earnings ratio of 25 times in 2026, the target price is set at HK$104. The valuation logic is based on the improvement of the optical industry environment in 2024-2027. The average sales price (ASP) and profit margin of the company's products are expected to continue to increase, and the smart glasses business will become the second growth curve.
Risk warning:
Downside risks: Deterioration in consumer electronics demand led to downgrading product specifications, falling short of expectations in the iPhone market share, and slowing down in automotive ADAS penetration;
Upside risks: Smart glasses camera module ASP increase, automotive business orders exceed expectations, industry competition pattern optimization.
Interpretation of key charts: 2025-2030 smart glasses shipment growth rate forecast
Industry risk tips
Technology implementation risk: The display effect and battery life of AR glasses still do not meet consumer-grade expectations. If the pace of technology iteration slows down, it may delay the industry's explosion;
Risk of supply chain fluctuations: Core components (such as micro OLED screens) rely on Japanese and Korean companies. If geopolitical or capacity issues cause supply shortages, it will affect industry shipments;
Demand falls short of risk: If the macroeconomy continues to weaken and the consumer electronics switching cycle is extended, demand for smart glasses may fall short of expectations;
Competition increases risk: More tech giants (such as Apple and Huawei) entering the market may trigger price wars and squeeze the profit margins of small and medium-sized suppliers.
 Index Options
Index Options State Street
State Street CME Group
CME Group Nasdaq
Nasdaq Cboe
Cboe TradingView
TradingView Wall Street Journal
Wall Street Journal