IPO Foresight | If we want to create a new growth point with power device products, can Xinmai Semiconductor's profit side return to the growth trajectory?
Power semiconductors can minimize energy consumption and improve the performance of automobiles, renewable energy infrastructure, and industrial equipment, so they are widely used in consumer electronics, industrial applications, and automobiles, providing smarter, more efficient, and reliable solutions for modern electrification needs.
As more and more devices and systems are electrified, the role of power semiconductors is becoming more and more prominent. Companies including Silanwei, China Resources, and Star Semiconductor continue to lead the continuous growth of China's power semiconductor industry with the attitude of leading the industry.
Recently, a company from the field of power semiconductors began a listing journey in Hong Kong. The Zhitong Finance App observed that, founded in 2019, Xinmai Semiconductor, headquartered in Hangzhou, submitted a prospectus to the Hong Kong Stock Exchange on June 30 to apply for listing on the main board. Huatai International is the sole sponsor.
According to Frost & Sullivan data, based on total shipments over the past ten years, Xinmai Semiconductor ranked first in the global OLED display PMIC (power management integrated circuit) market; in terms of revenue in 2024, Xinmai Semiconductor ranked 2nd in the global OLED display PMIC market and 3rd in the global smartphone PMIC market. It can be seen from this that Xinmai Semiconductor has broken into the first tier of the industry in the global smartphone PMIC market and the OLED display PMIC market.
However, judging from performance, Xinmai Semiconductor's performance on the profit side is not optimistic. From 2022 to 2024, Xinmai Semiconductor's revenue was 1,688 billion yuan (RMB, same below), 1.64 billion yuan, and 1,574 billion yuan respectively, showing a slight downward trend; adjusted net profit for the same period was 238 million yuan, 76.923 million yuan, and -53.334 million yuan, respectively. Net profit continued to decline sharply and changed from profit to loss.
This kind of performance may have a certain impact on Xinmai Semiconductor's IPO valuation, but the key question is, why has the profit side of Xinmai Semiconductor changed so much in just 3 years? Can it be improved in the future?
Nearly 70% of revenue comes from overseas markets
In 2018, the domestic semiconductor industry set off a wave of domestic substitution under the US blockade. Taking this opportunity, Xinmai Semiconductor was established in Hangzhou in September 2019. By 2020, Xinmai Semiconductor acquired SMI, a Korean company focusing on power management ICs, to enter the power semiconductor circuit and recruit SMI founder Dr. Huh Youm (Executive Vice President of Qianhai Lux) to join the company's core team.
Looking at the business model, Xinmai Semiconductor defines itself as a new Fab-Lite integrated equipment manufacturer (IDM), which means it is a vertically integrated power semiconductor company integrating IC design, manufacturing, and sales. Fab-Lite, on the other hand, is a light fab. This is a new IDM variant. Its core feature is to balance costs and autonomous controllability through partial outsourcing of manufacturing processes.
Up to now, Xinmai Semiconductor's core business covers research, development and sales of power management ICs and power devices in the field of power semiconductors. The company's products cover the three major fields of mobile technology, display technology, and power devices, and are widely used in many fields such as automobiles, telecommunications equipment, data centers, industrial applications, and consumer electronics.
In terms of revenue structure, power management ICs are the most important source of revenue for Xinmai Semiconductor. In 2024, revenue from power management IC products accounted for 90.7% of the company's total revenue, with mobile accounting for 48.5%, showing 42.2%. Power device products, on the other hand, account for only 9.3% of revenue.
However, the year-on-year decline in the revenue side of Xinmai Semiconductor is due to the continued decline in revenue from power management IC products sold overseas. According to the prospectus, the revenue of Xinmai Semiconductor's power management IC products from 2022 to 2024 was 1,655 billion yuan, 1,597 billion yuan, and 1,428 billion yuan respectively, with a clear downward trend. Moreover, both mobile and display products continue to decline.
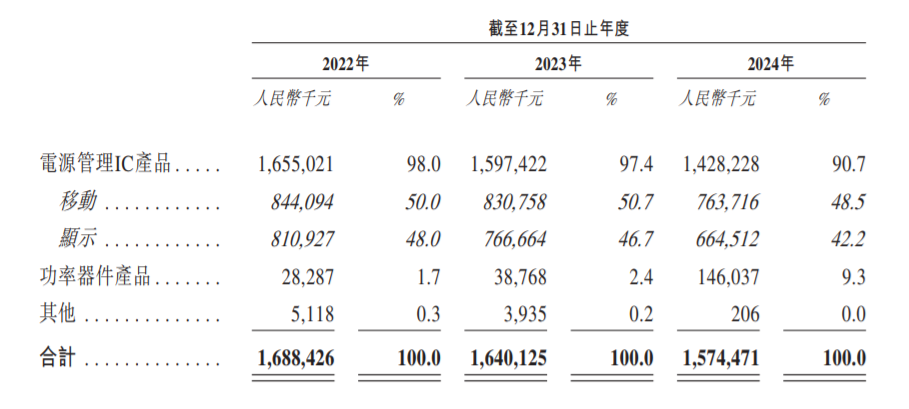
If you look at the geographical division, the continued decline in Xinmai Semiconductor's revenue is due to the continuous decline in revenue from overseas. According to the prospectus, nearly 70% of Xinmai Semiconductor's revenue is from overseas markets. From 2022 to 2024, its revenue from overseas markets was 1,231 billion yuan, 1,216 billion yuan, and 1,072 billion yuan, respectively.
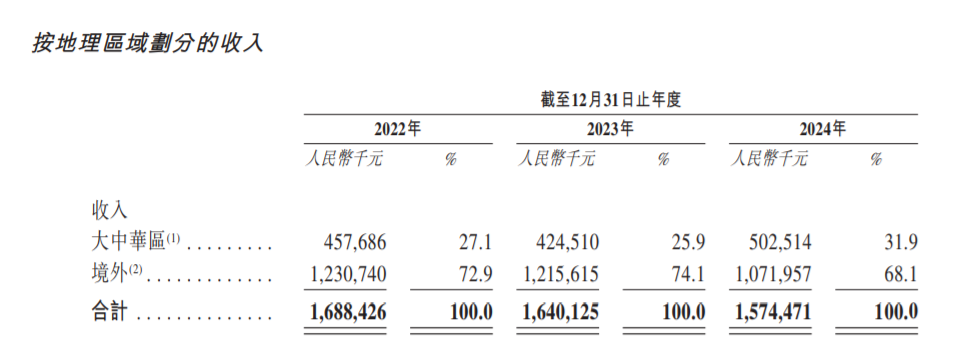
The comprehensive revenue structure and geographical area is easy to find that the decline in revenue from power management IC products sold overseas by Xinmai Semiconductor has dragged down the company's overall revenue performance. Xinmai Semiconductor also stated in its prospectus that this is mainly due to overseas customers facing weak downstream consumer demand and the downturn in the consumer electronics market.
But behind this, it also revealed Xinmai Semiconductor's excessive dependence on leading customers. According to the prospectus, in 2024, Xinmai Semiconductor's top five customers accounted for 77.6% of revenue, and customer A's share was as high as 61.4%. In 2022 and 2023, customer A's revenue share was as high as 66.7% and 65.7%.

Continued high investment in R&D to create a new growth curve with power device products
In fact, excessive reliance on a single customer will not only lead to increased fluctuations on the revenue side, but may also cause problems such as imbalances in bargaining power and difficulties in raising product prices. Especially when market competition intensifies, companies often need stronger price cuts to stabilize business relationships.
According to the prospectus, due to increased competition in overseas markets, the gross margins of Xinmai Semiconductor's power management IC products from 2022 to 2024 were 38.1%, 36.1%, and 32.9% respectively, falling 5.2 percentage points over two years, which put pressure on the profitability of the company's power management IC business.
Judging from the overall gross margin data, the decline in Xinmai Semiconductor's gross margin is even more obvious. According to the data, from 2022 to 2024, Xinmai Semiconductor's overall gross margin was 37.4%, 33.4%, and 29.4% respectively, falling 8 percentage points over two years. In addition to being dragged down by power management IC products, the gross loss of power device products also affected the overall gross margin level.
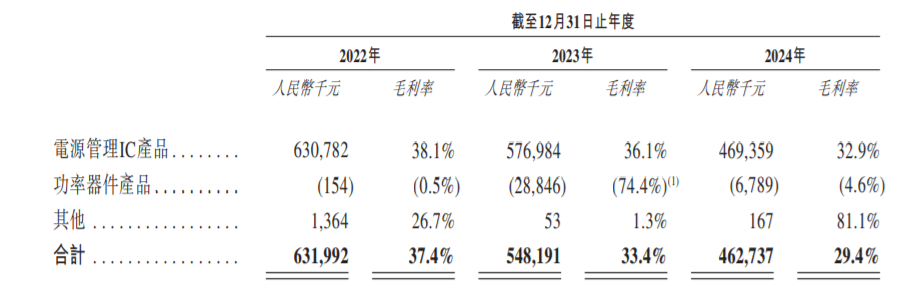
This also does not prohibit the market from being curious. Why is the gross margin of power management IC products as high as 30%, while power device products record gross losses. The first is that power device products face the domestic market, and the domestic market competition is fierce, and the gross margin is relatively low; the second is that the shipping scale of power device products is still not large enough, so the scale effect has not been fully exploited. As a result, power device products put further pressure on Xinmai Semiconductor's gross margin.
At the same time as revenue and gross margin continued to decline, Xinmai Semiconductor's three expenses (sales and marketing expenses, general and administrative expenses, R&D expenses) continued to rise. As a result, the company's net profit declined. The data showed that from 2022 to 2024, Xinmai Semiconductor's three expenses accounted for 27.2%, 36.8%, and 45.1% of revenue, respectively. The rapid rise in three-fee expenses seriously damaged the net profit side of Xinmai Semiconductor. In particular, in 2024, it directly caused an adjusted net profit loss of 53.334 million yuan.

However, behind the shift in adjusted net profit from profit to loss, it also reflects Xinmai Semiconductor's response in the face of declining demand from a single major customer, that is, to open up a new growth curve with power device products in the domestic region, and the expansion of new business will naturally drive an increase in expenses. This is even more obvious in terms of R&D expenses. From 2022 to 2024, Xinmai Semiconductor's R&D expenses accounted for 14.6%, 20.5%, and 25.8% of the company's total revenue, respectively. Obviously, Xinmai Semiconductor attaches great importance to the company's R&D.
However, judging from the results, Xinmai Semiconductor's share of power semiconductor revenue in 2024 was 9.3%, and the gross margin was -4.6%. Although there is a significant improvement from 2023, it remains to be seen whether it can further expand and strengthen in the highly competitive domestic market. The slope of revenue growth in the power device product business and the rate at which gross margin increases will be key factors in determining Xinmai Semiconductor's valuation level.
 Index Options
Index Options State Street
State Street CME Group
CME Group Nasdaq
Nasdaq Cboe
Cboe TradingView
TradingView Wall Street Journal
Wall Street Journal