Mani (TSE:7730) Strong Profits May Be Masking Some Underlying Issues
Mani, Inc.'s (TSE:7730) robust recent earnings didn't do much to move the stock. We believe that shareholders have noticed some concerning factors beyond the statutory profit numbers.
Check out our latest analysis for Mani
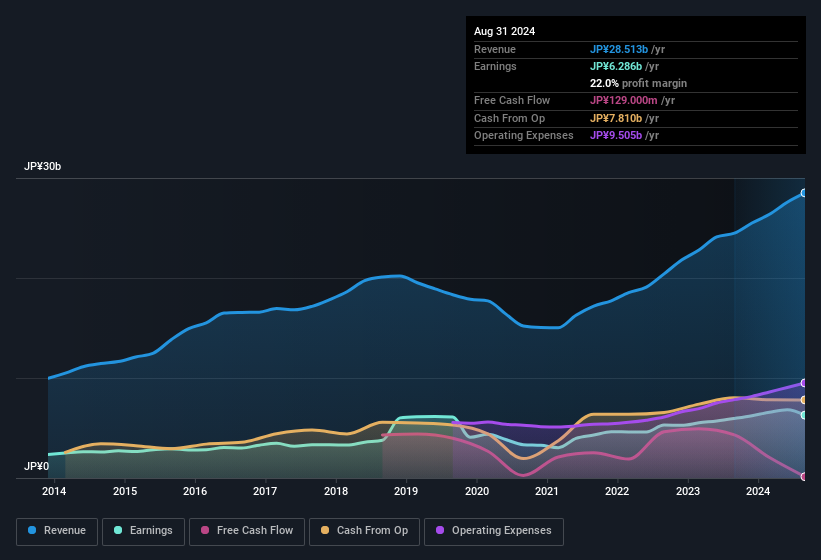
Examining Cashflow Against Mani's Earnings
In high finance, the key ratio used to measure how well a company converts reported profits into free cash flow (FCF) is the accrual ratio (from cashflow). In plain english, this ratio subtracts FCF from net profit, and divides that number by the company's average operating assets over that period. You could think of the accrual ratio from cashflow as the 'non-FCF profit ratio'.
As a result, a negative accrual ratio is a positive for the company, and a positive accrual ratio is a negative. While it's not a problem to have a positive accrual ratio, indicating a certain level of non-cash profits, a high accrual ratio is arguably a bad thing, because it indicates paper profits are not matched by cash flow. Notably, there is some academic evidence that suggests that a high accrual ratio is a bad sign for near-term profits, generally speaking.
Over the twelve months to August 2024, Mani recorded an accrual ratio of 0.22. We can therefore deduce that its free cash flow fell well short of covering its statutory profit. In fact, it had free cash flow of JP¥129m in the last year, which was a lot less than its statutory profit of JP¥6.29b. Mani shareholders will no doubt be hoping that its free cash flow bounces back next year, since it was down over the last twelve months.
That might leave you wondering what analysts are forecasting in terms of future profitability. Luckily, you can click here to see an interactive graph depicting future profitability, based on their estimates.
Our Take On Mani's Profit Performance
Mani didn't convert much of its profit to free cash flow in the last year, which some investors may consider rather suboptimal. Because of this, we think that it may be that Mani's statutory profits are better than its underlying earnings power. Nonetheless, it's still worth noting that its earnings per share have grown at 46% over the last three years. Of course, we've only just scratched the surface when it comes to analysing its earnings; one could also consider margins, forecast growth, and return on investment, among other factors. With this in mind, we wouldn't consider investing in a stock unless we had a thorough understanding of the risks. To that end, you should learn about the 2 warning signs we've spotted with Mani (including 1 which is a bit concerning).
This note has only looked at a single factor that sheds light on the nature of Mani's profit. But there is always more to discover if you are capable of focussing your mind on minutiae. Some people consider a high return on equity to be a good sign of a quality business. So you may wish to see this free collection of companies boasting high return on equity, or this list of stocks with high insider ownership.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
 Index Options
Index Options CME Group
CME Group Nasdaq
Nasdaq Cboe
Cboe TradingView
TradingView Wall Street Journal
Wall Street Journal