What is Qualitative Fundamental Analysis
What is qualitative analysis?
Qualitative analysis is a way to analyze a company's value or prospect by subjective judgment and experience on the non-quantifiable fundamental data. The non-quantifiable information may tell the nature of a company, such as the business model and its target customers. It may also describe the industry environment or economic condition affecting an individual company's profitability and activity.
The qualitative analysis differs from quantitative analysis in measurement—the former talks about non-numeric information like the examples used above, and the latter focuses on the data represented as a number, like financial ratios. In most cases, investors may apply qualitative and quantitative analysis together to examine the trajectory and potential of a company and determine investment opportunities.
How to start qualitative analysis
Investors may start a qualitative analysis with data collection from many sources. Many consider the narrative section of a company report as an excellent source to gain a big picture of the company, especially the management discussion and analysis section. Meanwhile, you might also get insights from newspaper articles, social media, news outlets, and blog posts. Such information should be handled with care, for they are less reliable than the required disclosure.
Next, investors need to organize and process the data logically and meaningfully. This step largely relies on the investors' intuition and experience through proper analytical reasoning to reach a rough judgment of a company and its future development. And the follow-up in updating the data is necessary to determine whether it affects or changes your previous assessment.
Here, we introduce three commonly used concepts to help you apply the qualitative analysis.
Porter's five forces theory
There is an inherent different degree of competition among various industries. Some industries are highly competitive, with most players struggling to earn adequate returns on capital. In contrast, other industries with high barriers may allow the industry participants to generate healthy profits.
Michael Porter, a Harvard Business school professor, developed a framework that identified five determinants of the intensity of competition in an industry:
- The threat of entry
- The power of suppliers
- The power of buyers
- The threat of substitutes
- The rivalry among existing competitors

As a framework, Porter's five forces theory analyzes a competitive landscape and attractiveness for the industry to help understand a company's operation activity as a part of an industry.
SWOT analysis
While Poter's five forces theory focuses mainly on competition rivalry in an industry, SWOT analysis concentrates on an individual target company. The SWOT analysis framework facilitates identifying the internal strategic factors (strengths and weaknesses) and external strategic factors (opportunities and threats). It leads to a 2X2 matrix – also known as SWOT Matrix.
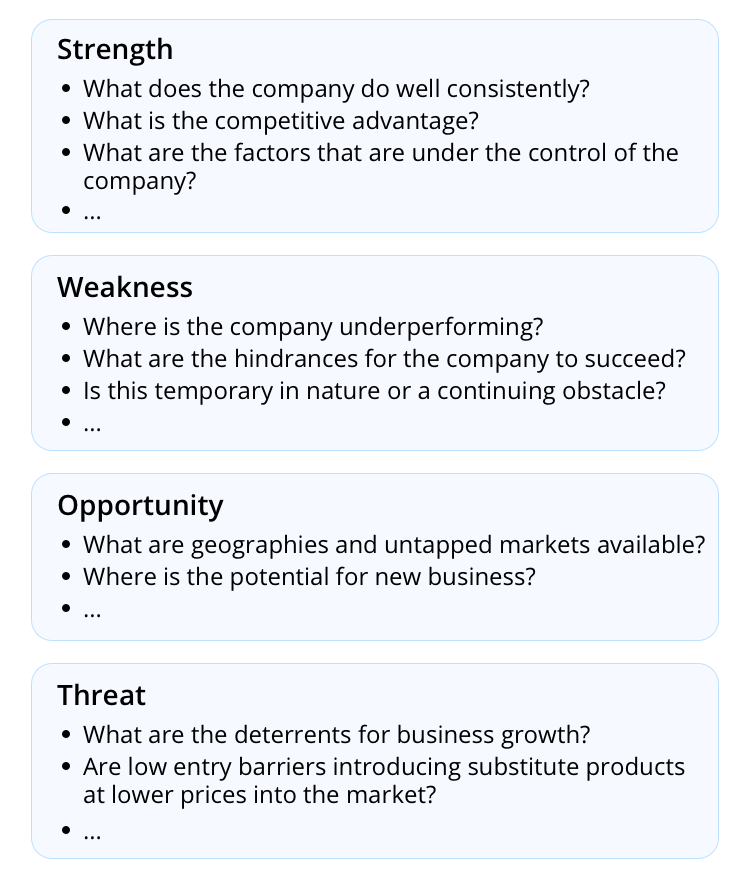
Even though some companies operate in the same industry, their performances differ. The SWOT analysis will help investors understand the target company comprehensively and make better investment decisions.
PEST analysis
PEST analysis describes a company's business environment from FOUR perspectives: political, economic, social, and technological. This method comprehensively analyses external factors that could affect every company.

 Index Options
Index Options State Street
State Street CME Group
CME Group Nasdaq
Nasdaq Cboe
Cboe TradingView
TradingView Wall Street Journal
Wall Street Journal